[Machine Learning] Logistic Regression
Skim through fundamental machine learning concepts and mathematical implications.
Logistic Regression
Logistic Regression is a binary classification model labels a sample to Class 1 if the probability exceeds 50%, and labels it to Class 0 if not.
$\beta_0 + \beta_1x_1 + … + \beta_kx_k = p$
Domain = (-inf, + ing)
Range = [0, 1]
Predicit $logit = ln\frac{p}{1-p}$ to match Domain and Range.
$\beta_0 + \beta_1x_1 + … + \beta_kx_k = ln\frac{p}{1-p}$
$\therefore p = \frac{1}{1 + e^{-(\beta_0 + \beta_1x_1 + … + \beta_kx_k)}}$
Sigmoid Function
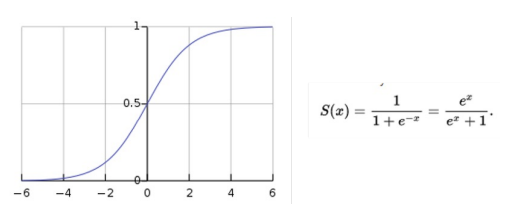
$\frac{1}{1 + e^{-(\beta_0 + \beta_1x_1 + … + \beta_kx_k)}} = Sigmoid Function$
Sigmoid Function returns any values to value range from $0$ to $1$.
import numpy as np
def sigmoid(x):
return 1/(1 + np.exp(-x))
Loss Function
Logistic Regression predicts regression coefficients by Maximum Likelihood Estimates.
$Max$ $Likelihood$ = $\Pi p(x_i) \Pi (1 - p(x_i))$
$\Pi p(x_i)$ : probability of predicting 1 for actual 1
$\Pi (1 - p(x_i))$ : probability of predicting 0 for actual 0
$Min$ $Loss$ = $-\Sigma y_iln(p(x_i)) + (1 - y_i)ln(1 - p(x_i))$

댓글남기기