transformer-chatbot
Tensorflow tutorial을 참고하여 만든 transformer모델 기반 한국어 심리상담 챗봇 미니 프로젝트입니다.
ipynb 파일 폴더 : https://github.com/a2ran/kor-eng-translator
참고문헌 : https://www.tensorflow.org/text/tutorials/transformer
사용 데이터셋: 웰니스 대화 스크립트 데이터셋(AI Hub, 2019)
한국어 문장 형태소 분석
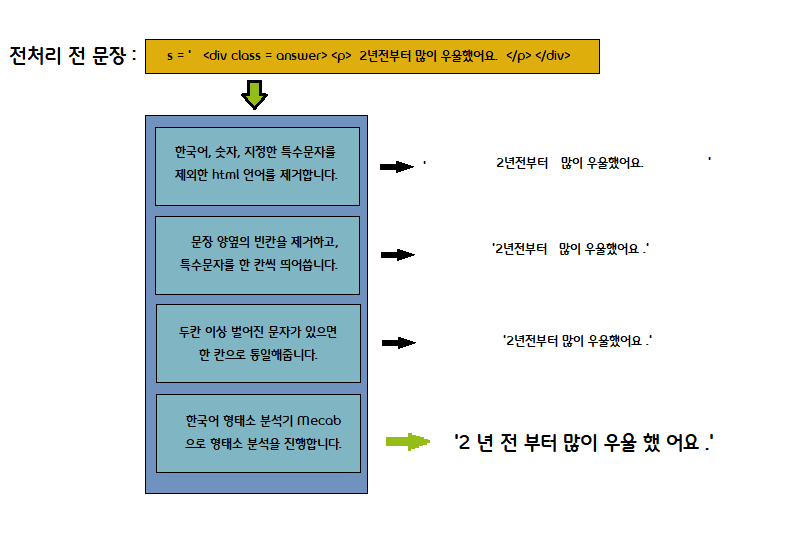
텍스트를 토큰화 하기 전, 주어진 문장을 전처리하고 형태소를 분리합니다.
원하지 않는 특수문자들을 제거해 불용어로 인한 오류를 줄일 수 있고,
단어를 형태소 단위로 분리해 사용자의 발화를 더욱 잘 파악할 수 있습니다.
전처리 코드
# 한국어 형태소 분석기 Mecab을 정의합니다.
from eunjeon import Mecab
import re
m = Mecab()
def reg_kor(sentence):
# 한국어, 숫자, 지정한 특수문자를 제외한 html 언어를 제거합니다.
sentence = re.sub('[^0-9가-힣!?,.()]', ' ', sentence)
# 문장 양옆의 빈칸을 제거하고, 특수문자를 한 칸씩 띄어씁니다.
sentence = re.sub(r"([,.?!])", r" \1", sentence.strip())
# 두 칸 이상 벌어진 문자가 있으면 한 칸으로 통일해줍니다.
sentence = re.sub(r'[" "]+', " ", sentence)
# 한국어 형태소 분석기 mecab으로 형태소 분석을 진행합니다.
sentence = " ".join(m.morphs(sentence))
return sentence
전처리 결과
Input & Output Embeddings
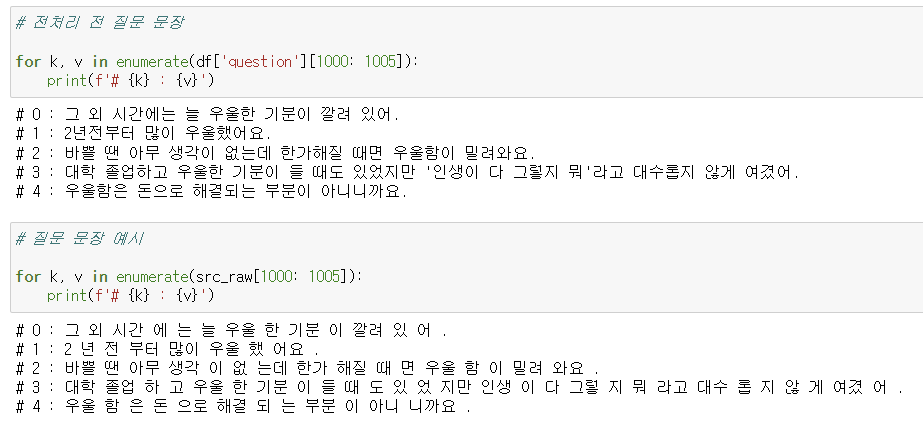
비정형 데이터인 시퀀스 문장 데이터를 transformer으로 학습하기 위해서는
문장을 토큰화한 후 임베딩한 후 인코더 모델에 학습시킬 입력 변수 src,
context_vector와의 가중평균을 decoder에 넘겨줄 타겟 변수 tgt_inputs,
다음 단어를 예측하는데 사용할 레이블인 tgt_labels 변수로 나누어주었습니다.
tgt_inputs은 label보다 한 단어 앞서 예측에 필요한 정보를 제공해야 하므로 [start] 토큰부터,
tgt-labels은 예측의 대상이므로 tgt_inputs보다 한 단어 늦게 시작해 [end] 토큰까지 받습니다.
임베딩 코드
# Train, Validation 데이터셋을 zero-padded 토큰으로 변화합니다.
# Transformer 모델에 사용하기 위해 한 단어의 텀을 가진 tgt_inputs, tgt_labels 변수를 분리하고,
# tgt_in 변수와 src 변수를 묶어줍니다.
MAX_TOKENS = 128
def prepare_batch(src, tgt):
src = src_text_processor(src)
src = src[:, :MAX_TOKENS]
src = src.to_tensor()
tgt = tgt_text_processor(tgt)
tgt = tgt[:, :(MAX_TOKENS + 1)]
tgt_inputs = tgt[:, :-1].to_tensor() # Drop [END] tokens
tgt_labels = tgt[:, 1:].to_tensor() # Drop [start] tokens
return (src, tgt_inputs), tgt_labels
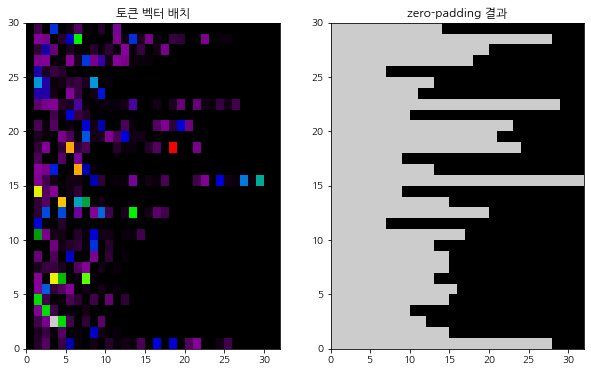
데이터 임베딩 + zero-padding 결과
zp = src_text_processor(src_raw[:30])
plt.figure(figsize = (10, 6))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.pcolormesh(zp.to_tensor(), cmap = 'nipy_spectral')
plt.title('토큰 벡터 배치')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.pcolormesh(zp.to_tensor() != 0, cmap = 'nipy_spectral')
plt.title('zero-padding 결과')
Positional Encoding
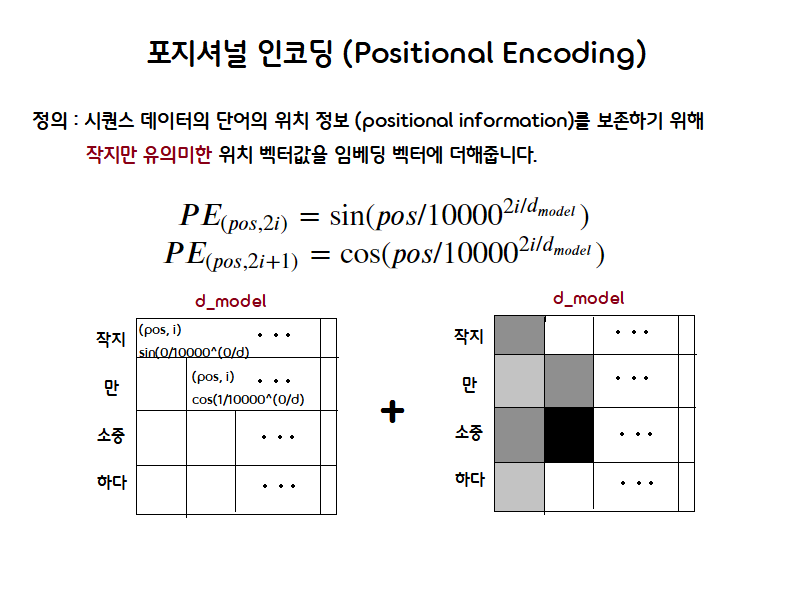
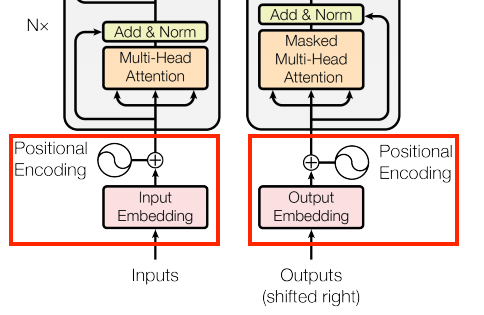
사진출처: https://www.tensorflow.org/text/tutorials/transformer
코드 예시
#length = sentence에 존재할 수 있는 maximum amount of tokens (length = 2048)
#depth = dimension of th emodel (d_model = 512)
# i = ~ depth/2 = [0, ..., 255]
def positional_encoding(length, depth):
# d_model/2
depth = depth/2
# pos = 토큰의 위치 [0, ..., 2047]
positions = np.arange(length)[:, np.newaxis] # (seq, 1)
# i / (d_model/2) = 2i/d_model
depths = np.arange(depth)[np.newaxis, :]/depth # (1, depth)
# 1/10000^(2i/d_model)
angle_rates = 1 / (10000**depths) # (1, depth)
# pos/(10000)^(2i/d_model)
angle_rads = positions * angle_rates # (pos, depth)
#[sin(0), cos(0)], [sin(2), cos(2)]....
pos_encoding = np.concatenate(
[np.sin(angle_rads), np.cos(angle_rads)],
axis = -1)
# encoding한 값을 float으로 반환합니다.
return tf.cast(pos_encoding, dtype = tf.float32)
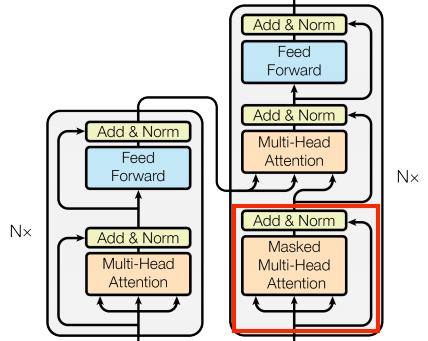
Base Attention Layer

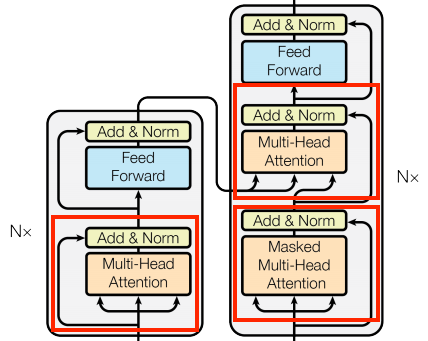
코드 예시
# attention layer에 상속할 base attention layer을 정의합니다.
class BaseAttention(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super().__init__()
# Define multihead attention layer
self.mha = tf.keras.layers.MultiHeadAttention(**kwargs)
# Define normalization layer = LayerNorm()
self.layernorm = tf.keras.layers.LayerNormalization()
# Define addition layer = (x + sublayer(x))
self.add = tf.keras.layers.Add()
Cross Attention Layer
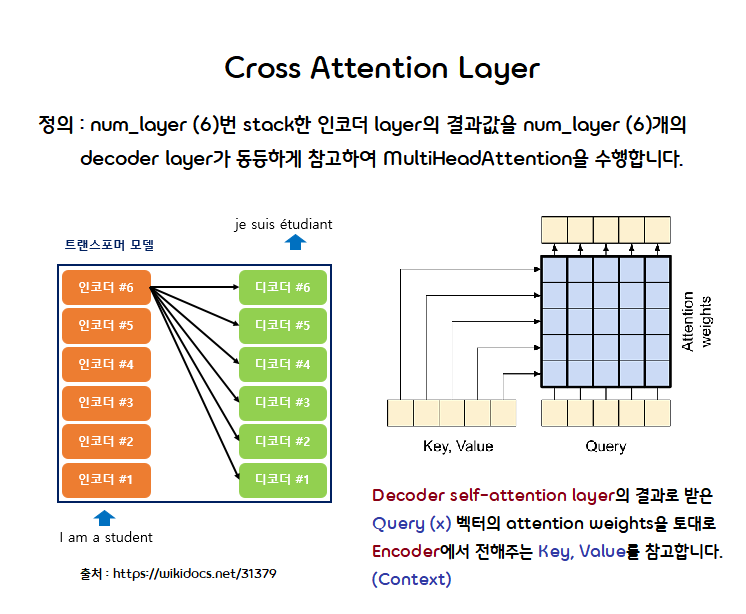
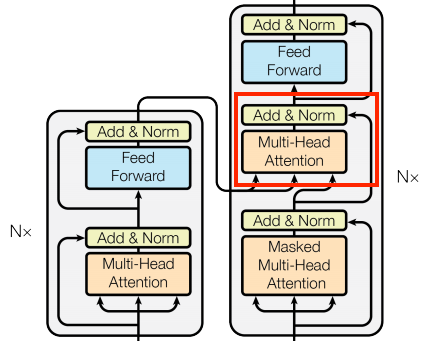
코드 예시
# Encoder의 결과값을 Decoder로 넘겨주는 attention layer입니다.
# BaseAttention의 클래스를 상속합니다.
class CrossAttention(BaseAttention):
# self-attention layer에서 x를, encoder에서 key, value를 받아옵니다.
def call(self, x, context):
attn_output, attn_scores = self.mha(query = x,
key = context,
value = context,
return_attention_scores = True)
self.last_attn_scores = attn_scores
# Output (x) = LayerNorm(x + sublayer(x))
x = self.add([x, attn_output])
x = self.layernorm(x)
return x
Self-Attention Layer
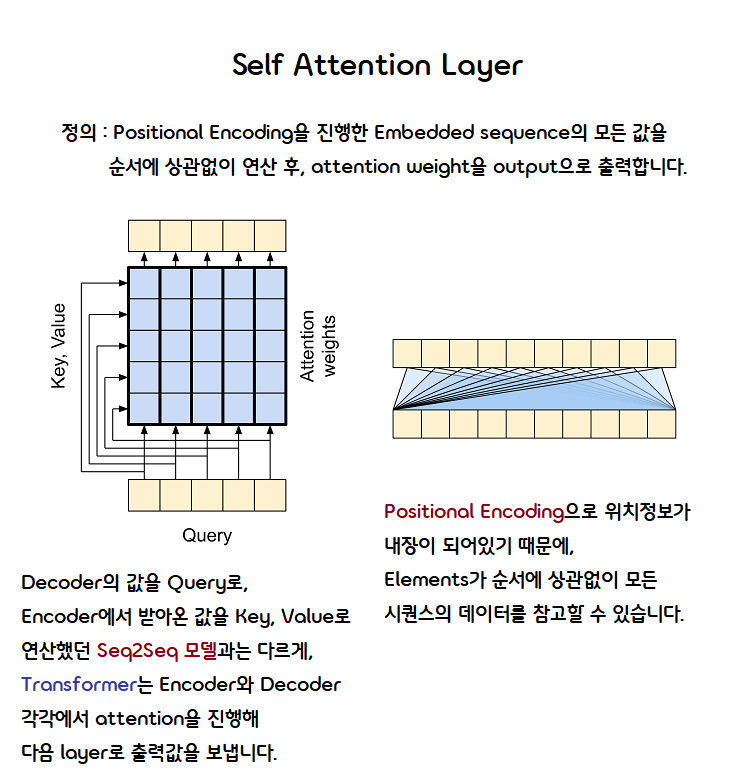
코드 예시
class GlobalSelfAttention(BaseAttention):
# Encoder, Decoder 각각에서 Query, Value, Key 값을 가져옵니다.
def call(self, x):
attn_output = self.mha(query = x,
value = x,
key = x)
# Output (x) = LayerNorm(x + sublayer(x))
x = self.add([x, attn_output])
x = self.layernorm(x)
return x
Feed Forward Layer

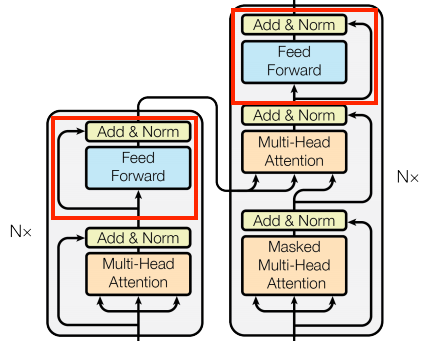
코드 예시
# one-layer feedforward layer
# dff (2048) -> d_model (512)
class FeedForward(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, d_model, dff, dropout_rate=0.1):
super().__init__()
self.seq = tf.keras.Sequential([
# 2048, relu
tf.keras.layers.Dense(dff, activation='relu'),
# 2048 -> 512
tf.keras.layers.Dense(d_model),
# 0.1만큼 overfitting 방지
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(dropout_rate)
])
self.add = tf.keras.layers.Add()
self.layer_norm = tf.keras.layers.LayerNormalization()
def call(self, x):
# Output (x) = LayerNorm(x + sublayer(x))
x = self.add([x, self.seq(x)])
x = self.layer_norm(x)
return x
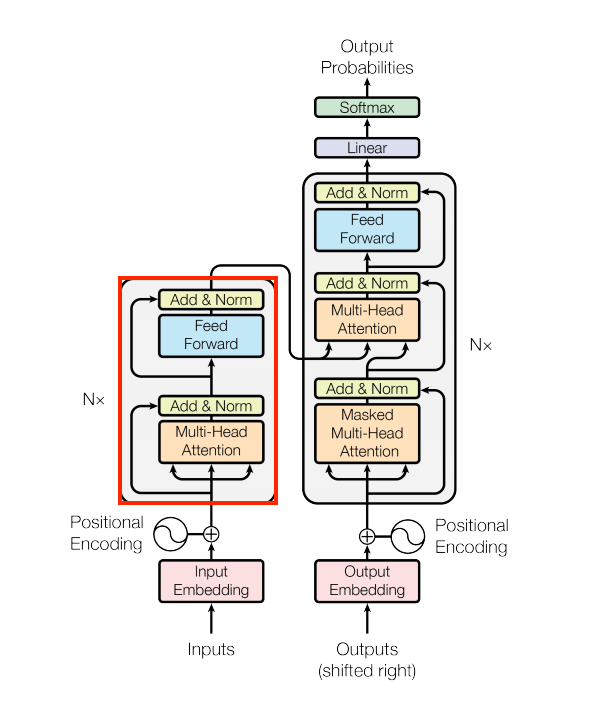
Encoder Layer

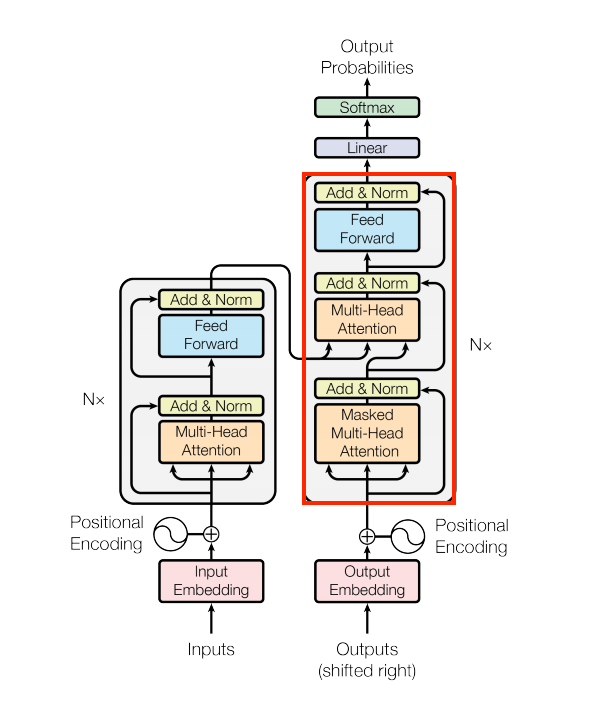
Decoder Layer

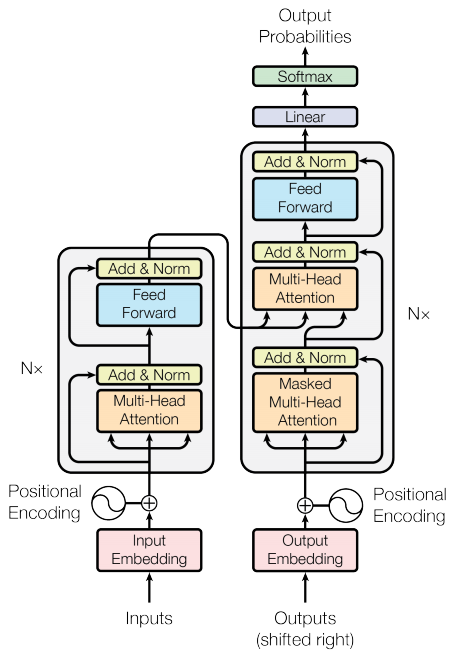
Transformer

Train model
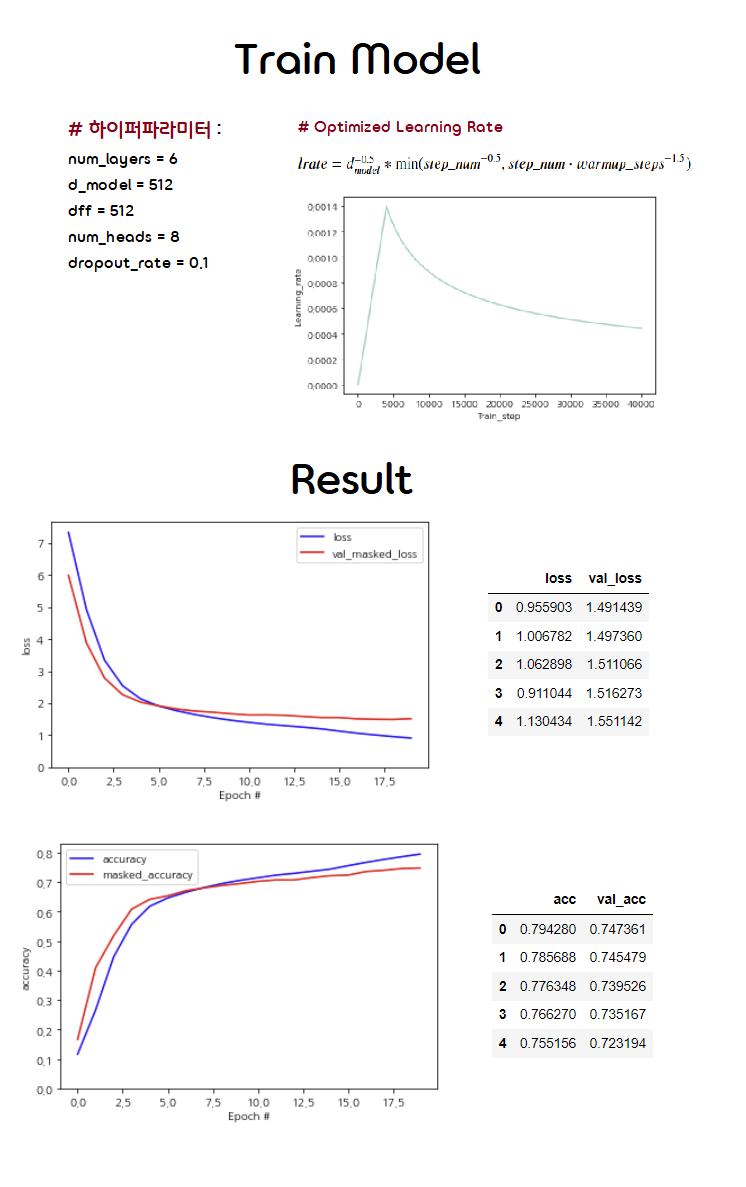
Hyperparameters
num_layers = 6
d_model = 512
dff = 512
num_heads = 8
dropout_rate = 0.1
epochs = 20
Attention Plots

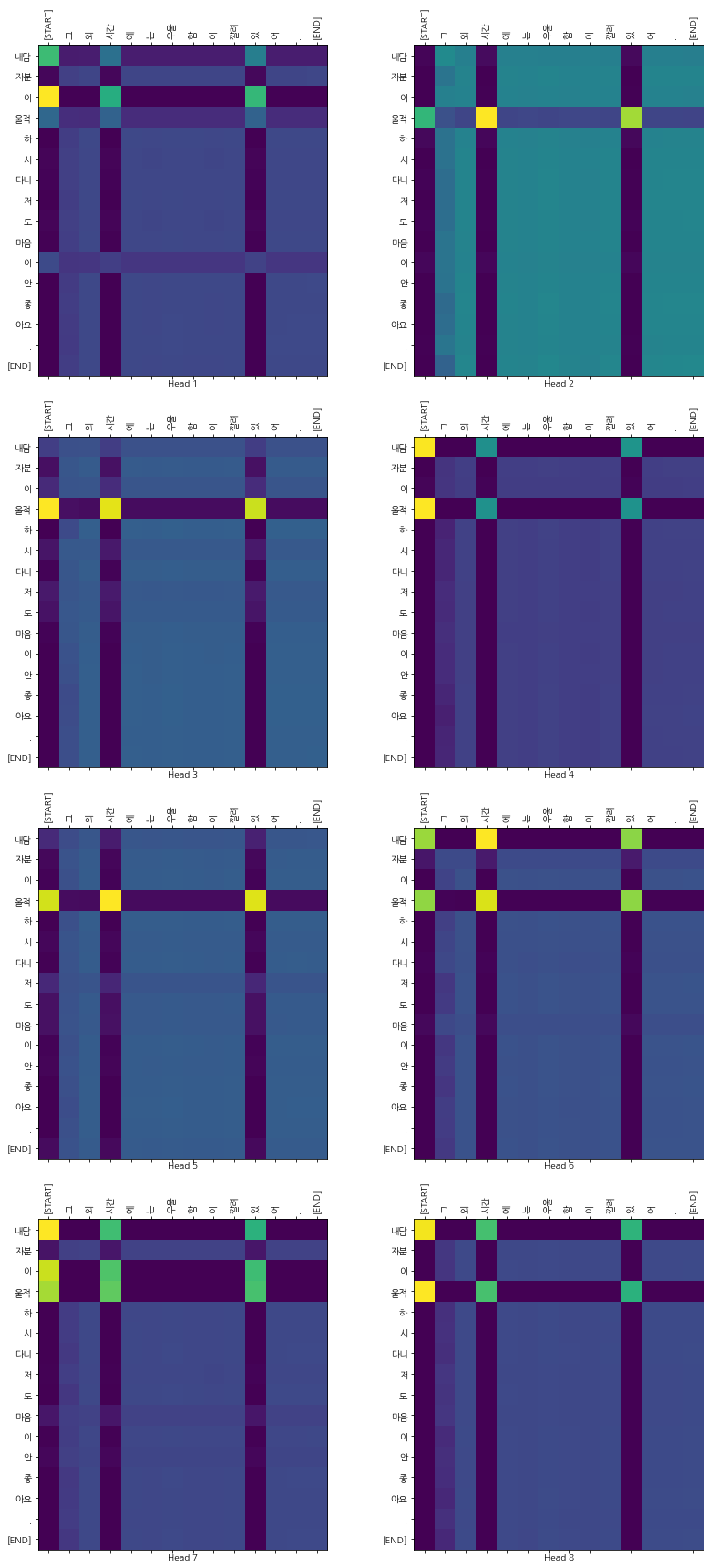
Predict new sentences


댓글남기기